· 06/07/2024 ·
Intel® Trust Authority sample workload for Intel® TDX
The sample confidential computing workload for Intel® Trust Domain Extensions (Intel® TDX) demonstrates the secure key release use case and the passport attestation model. The sample is provided in two Docker containers, a relying party and an attesting workload. Intel® Trust Authority is the verifier. The open-source code for this sample is available on GitHub in the intel/trustauthority-samples repo.
Secure key release workflow
In this sample, the secure key release workflow operates in passport attestation mode. The Intel TDX workload (CW) is the attester, the KBS/KMS is the relying party, and Intel Trust Authority is the verifier. For more information about key release and passport attestation models, see Attestation Patterns.
This sample shows how to implement two important use cases: secure key release with passport attestation, and how to exchange a public key (or any binary or JSON data up to 1Mib) between the relying party and the attester. The sample workload is a machine learning (ML) model that is distributed as an encrypted blob. A key is needed to decrypt the blob and enable execution of the model.
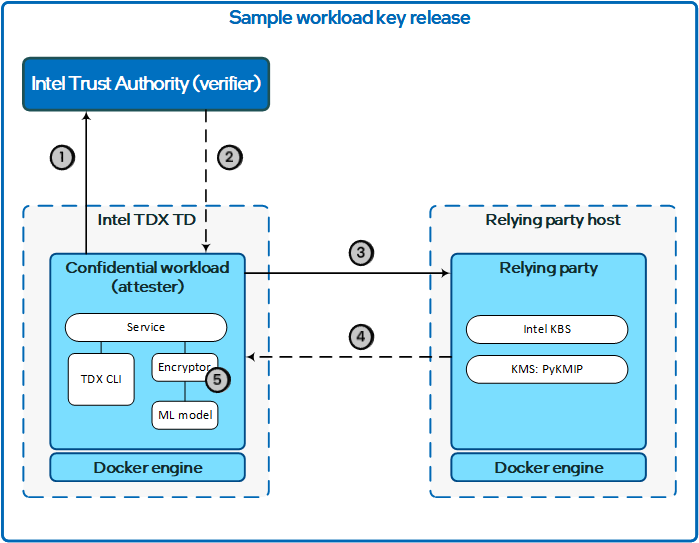
- The attesting workload obtains a quote from the Intel TDX TD by using the Intel Trust Authority CLI for Intel TDX ("TDX CLI"), which is also used to request an attestation token from Intel Trust Authority.
- The workload service creates an RSA key pair. The private key is retained by the service, and the public key is base64-encoded and then copied to the
--user-dataparameter in thetokencommand. The user data is output in the attester_held_data claim in the attestation token. The public key is used by the KBS to encrypt (encapsulate) the key request response body.
- The workload service creates an RSA key pair. The private key is retained by the service, and the public key is base64-encoded and then copied to the
- Intel Trust Authority evaluates the quote and returns an attestation token.
- The workload forwards the attestation token to Intel KBS in a REST API request for the decryption key needed to decrypt the ML model.
- The KBS evaluates the request and applies its key release policy. An Intel KBS key release policy compares values in the attestation token to reference values stored in the key release policy. If the key release policy evaluation is successful (that is, all compared values match), the KBS contacts the KMS to obtain the decryption key. The KMS will also apply its own key release policy, which is independent of the KBS policy. If the KMS policy allows, the KMS will return the requested key or secret to the KBS. The KBS uses the public key passed in the attestation token to wrap the KMS-supplied decryption key before sending it back to the workload.
- Intel KBS creates a symmetric AES key to encrypt the KMS-supplied key in the response body of a key request. This key is called the symmetric wrapping key (SWK). For enhanced security, Intel KBS can also use asymmetric key encapsulation with attestation tokens provided by Intel Trust Authority. Asymmetric key encapsulation uses a public key provided by the attester to encrypt the response body, including the SWK.
- The workload service decrypts the Intel KBS response by using the RSA private key from step 1.1. Then the service extracts the SWK from the response and uses it to decrypt the KMS-supplied key, which can then be used to decrypt the ML model. The model is now ready for use.
Intel TDX confidential workload
The Intel TDX CW comprises two main systems:
- A service layer that manages attestation and secure key release.
- A machine learning model that represents a confidential computing application. The model is assumed to contain confidential data and/or methodology, therefore it is encrypted. Before the Intel TDX client can decrypt the model for use, it needs to obtain a key for decryption from Intel KBS.
Intel KBS requires the workload to prove its identity and integrity to establish a trust relationship between the attesting workload and the relying party. Intel KBS compares the values in the attestation token included with the key release request to the values stored in a KBS key release policy. If the KBS policy evaluates to true, the requested key (or any secret, such as a connection string, access token, etc) is released to the requesting application.
The CW (confidential workload) is an encrypted blob. The encrypted CW can be provisioned with the TD VM or copied from a remote source after attestation. In this sample application, the CW is a machine learning (ML) model that's encrypted until the workload successfully obtains the key needed to decrypt the model for use.
The CW service manages tasks associated with attestation and decrypting the ML model.
- The service package manages the following:
- Creates an RSA key pair to encapsulate the key response from Intel KBS.
- Collects TD evidence and gets an attestation token by using the TDX CLI.
- Sends a request for a decryption key for the CW from Intel KBS (key release). The request includes the attestation token.
- Executes the CW's main function to decrypt & start the workload.
The service and CW are effectively platform-agnostic. The platform abstraction layer is the Intel TDX adapter version (must be installed) and the REST API endpoints, which can be set in a configuration file. Thus, the same CW code can be used on bare-metal Intel TDX or CSP VMs with Intel TDX, with no changes to the CW executive service or CC workload. The correct TEE adapter must be installed on the TD/VM, and this can be done during TD/VM deployment or provisioning.
Intel KBS relying party
In this sample, Intel® Trust Authority Key Broker Service (Intel KBS) is the relying party. Intel KBS is, as the name suggests, a broker between the workload and the key management system (KMS). Intel KBS doesn't store or manage keys and secrets; it relies on the key management system (KMS) to do that.
For this sample, Intel KBS uses PyKMIP for the KMS. PyKMIP is an open-source development tool with a simplified configuration and a relatively small footprint compared to other options. Both Intel KBS and PyKMIP support the Key Management Interoperability Protocol (KMIP).
Important
PyKMIP isn't a secure, production-quality KMS. Don't use PyKMIP for storing actual secrets. Intel KBS supports PyKMIP for development, and Hashicorp Vault (free or paid) for production use.
Sample components and setup
For build instructions, see the readmes in the GitHub repo.
- Dockerfile to build the Intel KBS relying party container.
- KBS.env environment file to configure the KBS. You must modify this file to suit your environment.
- Dockerfile to build the Intel TDX workload container. The Intel TDX workload build process supports Intel TDX hosts, Azure confidential VMs with Intel TDX, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Confidential VMs.
- workload.env to supply the workload with Intel KBS and Intel Trust Authority connection info. This file also contains secrets.
KBS environment file
The KBS.env file contains the settings needed to configure Intel KBS and PyKMIP.
Caution
KBS.env contains secrets including administrator password, KMS credentials, and an Intel Trust Authority attestation API key. To help secure your system you should delete the KBS.env file immediately after the initial configuration of the Intel KBS container. However, it's not necessary to delete the KBS.env file for the sample app if you're only using it as a learning tool.
When the relying-party container is run, a startup script configures Intel KBS to use the ADMIN_USERNAME and ADMIN_PASSWORD provided in the KBS.env file. You'll also need to provide an Attestation API key for TRUSTAUTHORITY_API_KEY, which you can get from the Intel Trust Authority portal.
LOG_LEVEL=INFO
KEY_MANAGER=kmip
ADMIN_USERNAME=<admin-username>
ADMIN_PASSWORD=<admin-password>
KMIP_VERSION=2.0
KMIP_SERVER_IP=127.0.0.1
KMIP_SERVER_PORT=5696
KMIP_CLIENT_KEY_PATH=/etc/pykmip/client_key.pem
KMIP_CLIENT_CERT_PATH=/etc/pykmip/client_certificate.pem
KMIP_ROOT_CERT_PATH=/etc/pykmip/ca_certificate.pem
PYKMIP_LOG_LEVEL=info
HTTPS_PROXY=<proxy url if required>
TRUSTAUTHORITY_BASE_URL=https://portal.trustauthority.intel.com
TRUSTAUTHORITY_API_URL=https://api.trustauthority.intel.com
TRUSTAUTHORITY_API_KEY=<API Key>
Note
The portal and API URLs for Intel Trust Authority differ by your region (US vs EU). Use the right URLs for your region:
| Region | BaseUrl | ApiUrl |
|---|---|---|
| World/US | https://portal.trustauthority.intel.com |
https://api.trustauthority.intel.com |
| EU | https://portal.eu.trustauthority.intel.com |
https://api.eu.trustauthority.intel.com |
Workload environment file
The workload.env file contains the settings needed for the sample workload to communicate with Intel KBS and Intel Trust Authority. This file contains secrets. Embedding secrets in an unencrypted file is not a recommended best practice for secure systems. It's done here to make the demo easy to configure.
The KBS_ADMIN and KBS_PASSWORD must match the ADMIN_USERNAME and ADMIN_PASSWORD used in KBS.env.
The KBS_URL is of the form https://<IP_address>:9443/kbs/v1, where IP_address is the IP address of the host machine where the relying-party (KBS) container is running. Port 9443 is the default listening port for Intel KBS.
SKIP_TLS_VERIFICATION if set to true will skip the TLS server certificate verification. For this demo, set it to true since we are using self-signed certificates for TLS.
TRUSTAUTHORITY_API_KEY is the same as used in KBS.env.
KBS_ADMIN=<KBS-admin-username>
KBS_PASSWORD=<KBS-admin-password>
KBS_URL=https://<KBS-IP>:9443/kbs/v1
SKIP_TLS_VERIFICATION=<true | false>
HTTPS_PROXY=<proxy url if required>
TRUSTAUTHORITY_API_URL=https://api.trustauthority.intel.com
TRUSTAUTHORITY_API_KEY=<API Key>
Run the workload
- Download the
sample-workload/execute_workload_flow.shscript for executing the secure key release workflow.wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/intel/trustauthority-samples/main/deployment/sample-workload/execute_workload_flow.sh - Run the following command to execute the workflow script.
bash execute_workload_flow.sh